Threaded fasteners are the backbone of countless industries, from construction and automotive to plumbing and manufacturing. With a myriad of thread types available, understanding their specific characteristics is crucial for ensuring the integrity and performance of any project.
One such thread type that stands out for its reliability and versatility is the NPT (National Pipe Thread). This blog post will delve into the world of NPT threads, exploring their definition, key characteristics, applications, and best practices for maintenance.
Let’s get started!
What are NPT Threads?
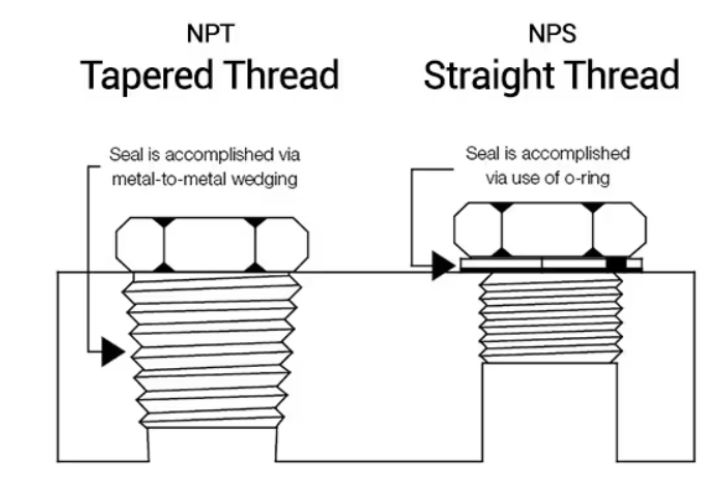
NPT, which stands for National Pipe Thread, is a standard for tapered threads used to connect pipes and fittings. It’s a widely recognized system in the United States and Canada. The NPT thread profile is characterized by its 60-degree angle and flat top and bottom.
The history of NPT threads dates back to the 19th century when standardization became crucial for industrial development. William Sellers, an American engineer, played a pivotal role in establishing the NPT standard, which eventually became the foundation for many other threaded connections.
Unlike other thread types like NPS (National Pipe Straight) which relies primarily on gaskets for sealing, NPT threads create a seal by the interference fit of the tapered male and female threads. This design ensures a tight and leak-resistant connection.
Key Characteristics of NPT Threads
The tapered design of NPT threads is essential for creating a tight seal. As the threads are tightened, the male part is drawn into the female part, compressing the metal and forming a seal. This makes NPT connections highly reliable in various applications.
It’s important to differentiate between hand-tight and tool-tight connections. While hand-tightening can be sufficient for some applications, most NPT connections require a wrench or pipe pliers for proper sealing.
NPT threads come in various sizes, with common ones including 1/8″, 1/4″, 3/8″, 1/2″, and 3/4 inches. The specific size is crucial for ensuring compatibility and proper fit.
Applications of NPT Threads
NPT threads are ubiquitous in numerous industries due to their reliability and versatility.
➡️ Plumbing and Pipe Fittings: This is perhaps the most common application. NPT threads are used to connect pipes, valves, and fittings for water, gas, and other fluids.
➡️ Industrial Equipment: Many industrial machines and systems rely on NPT connections for hydraulic and pneumatic components.
➡️ Automotive Industry: While less common than in other sectors, NPT threads can be found in certain automotive applications, such as fuel lines or coolant systems.
Beyond these primary areas, NPT threads have applications in various other industries, including agriculture, construction, and manufacturing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of NPT Threads
NPT threads offer several advantages:
➡️ Strong and Leak-Resistant Seals: The tapered design and interference fit create highly reliable seals.
➡️ Widely Available and Standardized: NPT threads are readily available, making them convenient to use.
However, there are also some drawbacks:
➡️ Can be Difficult to Disassemble: Removing an NPT connection can be challenging due to the tight seal.
➡️ Potential for Cross-Threading: Incorrect alignment can lead to cross-threading, damaging the threads.
NPT Thread Maintenance and Care
Proper installation is crucial for the longevity and performance of NPT threads. Using appropriate lubricants and sealants can enhance the sealing properties and make disassembly easier.
If leaks occur, it’s essential to identify the source of the problem, which might include loose connections, damaged threads, or incorrect sealant application.
When removing NPT fittings, using the right tools and techniques is vital to avoid damaging the threads.
FAQ
What is the difference between NPT and NPS threads?
➡️ NPT (National Pipe Taper) threads are tapered, creating a seal as they are tightened. NPS (National Pipe Straight) threads are parallel and require a separate sealing method like Teflon tape or pipe dope.
Can I use Teflon tape on NPT threads?
➡️ While Teflon tape can be used on NPT threads, it’s generally not necessary due to the inherent sealing capabilities of the tapered design. However, it can provide an extra layer of protection.
How do I know the size of an NPT thread?
➡️ NPT threads are typically measured by their nominal pipe size, such as 1/2 inch NPT. This refers to the approximate internal diameter of the pipe the fitting is designed for.
Can I reuse NPT fittings?
➡️ Reusing NPT fittings is generally not recommended as the sealing properties might be compromised. It’s best to use new fittings for reliable connections.
How tight should NPT connections be?
➡️ NPT connections should be tightened until they feel snug but not overly tight. Overtightening can damage the threads.
What is the best way to remove an NPT fitting?
➡️ To remove an NPT fitting, use a pipe wrench or adjustable wrench to grip the fitting while holding the pipe steady. Apply steady pressure while turning counterclockwise.
Can I mix NPT and BSP threads?
➡️ No, NPT and BSP (British Standard Pipe) threads are not compatible due to differences in thread profile and taper.
Conclusion
NPT threads are a fundamental component in many industries due to their ability to create strong and reliable seals. Understanding their characteristics, applications, and proper maintenance is essential for anyone working with threaded connections.
By carefully considering the advantages and disadvantages of NPT threads, you can make informed decisions about their suitability for your specific needs.
Post time: Aug-01-2024