In the world of engineering, precision is paramount. When it comes to threads, especially metric threads, accurate specification is crucial to ensure compatibility and reliability in various applications.
In this guide, we will delve into the intricacies of metric thread designation, uncovering the methods used to precisely specify metric threads and why it matters.
Understanding Metric Threads
Metric threads are a standardized system of thread design used in many parts of the world, including Europe and Asia. Unlike their imperial counterparts, which use inches and threads per inch (TPI), metric threads rely on millimeters and thread pitch to define their size and spacing. The two fundamental components of metric thread designation are the thread size and the thread pitch.
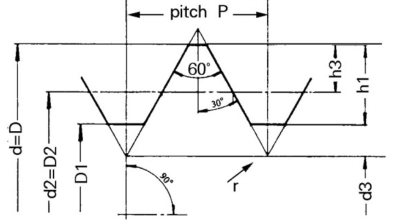
Metric Thread Profile with a 60-Degree Angle
1. Thread Size
The thread size is essentially the nominal diameter of the threaded portion of a fastener. In metric threads, this is typically expressed in millimeters (mm). For instance, if you have a bolt with a thread size of 6 mm, it means the bolt’s threaded portion has a nominal diameter of 6 millimeters.
2. Thread Pitch
Thread pitch refers to the distance between adjacent threads on a fastener. It is measured in millimeters as well and is a crucial aspect of metric thread designation. Essentially, it tells you how tightly spaced or coarse the threads are. For example, a metric thread with a pitch of 1.0 mm means that each thread is spaced 1.0 millimeter apart.
How Do You Specify Metric Threads?
Now that we understand the key components of metric threads, let’s explore how to specify them accurately.
1. Combining Thread Size and Pitch
To specify a metric thread, you need to provide both the thread size and the thread pitch. This combination offers a complete description of the thread. For instance, a metric thread designation of “M10x1.5” specifies a thread with a size of 10 mm and a pitch of 1.5 mm.
2. Use of Thread Designation
Metric thread designation is typically written in a specific format: “M” followed by the thread size and then the thread pitch. For example:
M8x1.0
M12x1.75
M20x2.5
This standardized format ensures that there is no ambiguity when communicating or selecting metric threads for a particular application.
3. Importance of Accuracy
Accurate metric thread specification is crucial to ensure that fasteners fit and perform as intended. Using the wrong thread size or pitch can result in insecure connections, improper sealing, or even damage to the components being fastened. Therefore, precision in thread designation is paramount, especially in critical applications such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing.
Conclusion: Mastering Metric Thread Designation
In the world of engineering, precision and accuracy are non-negotiable. Metric thread designation, with its emphasis on thread size and pitch, provides a standardized and reliable way to specify threads for various applications. By understanding and correctly using metric thread designations, engineers and manufacturers can ensure that their assemblies are secure, efficient, and reliable.
In conclusion, mastering metric thread designation is not just a matter of convenience; it is a fundamental aspect of engineering excellence.
Post time: Oct-27-2023